A03 - The chromatin remodelers ALC1 and HELLS regulate PARP dynamics and DNA repair
The anti-tumor potency of PARP inhibitors (PARPi) correlates with their “trapping” of PARP proteins on damaged chromatin. We found that the chromatin remodeling enzyme ALC1 (CHD1L) is actively required for the release of DNA damage-recruited PARP2 and that it potentiates the anti-cancer cell killing properties of clinical PARPi. We will now refine our understanding of ATP-fueled remodeler catalyze PARP2 release by determining how PARPi trap PARP2 using orthogonal biophysical assays, including HDX and live-cell imaging. Further, we will explore the synthetic lethal role of the remodeler HELLS (LSH), which mediates PARPi sensitization, and establish the molecular basis for its allosteric activation.
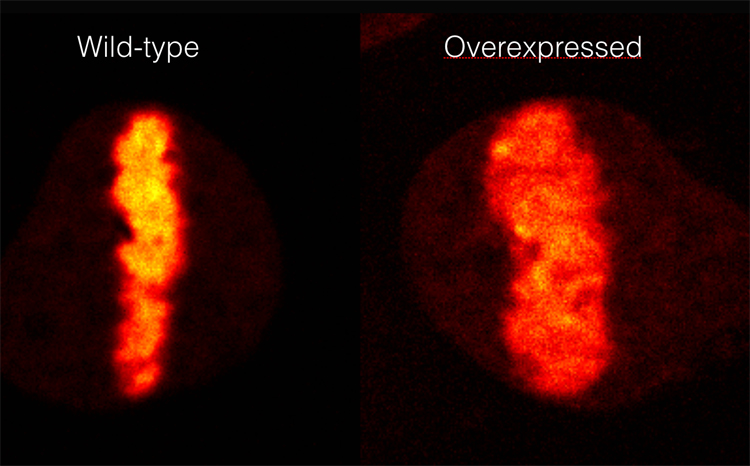
The human oncogene ALC1/CHD1L greatly decompacts chromatin structure upon UV-induced DNA damage. The chromatin at the DNA damage site is visualised using a photo-activatable histone H2B protein. The same chromatin region that is photo-activated is also damaged by the UV irradiation.

Prof. Andreas Ladurner, Ph.D.Biomedical Center Munich - Physiological Chemistry, LMU Munich +49 (0)89 2180 - 77095 |

